Hypercementosis
Hypercementosis is an idiopathic, non-neoplastic condition characterized by the excessive buildup of normal cementum (calcified tissue) on the roots of one or more teeth. A thicker layer of cementum can give the tooth an enlarged appearance, which mainly occurs at the apex or apices of the tooth.
Etiology
Occur in the apical area of the involved tooth following infection, chemical or mechanical trauma .
Or following local conditions such as periapical inflammatory processes , continuous dental eruption and functional stress due to occlusion forces ,
May also be associated with systemic endocrine [thyroid disease, acromegaly or skeletal disorders [Paget's disease.
Clinical & Radiographic features
Root hypercementosis is a frequent asymptomatic lesion in adults.
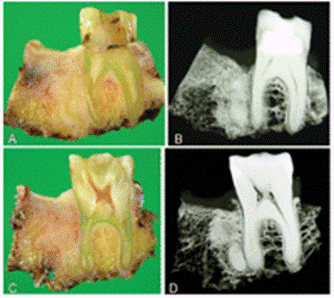
An excessive amount of cementum leading to abnormal thickness of the apex is easily detected both radiographically and macroscopically.
Typical findings are the excessive cementum formations around all or part of the root with superficial radiopaque lamina dura and the radiolucent shadow of the periodontal membrane similarly to normal cementum
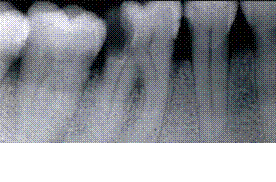
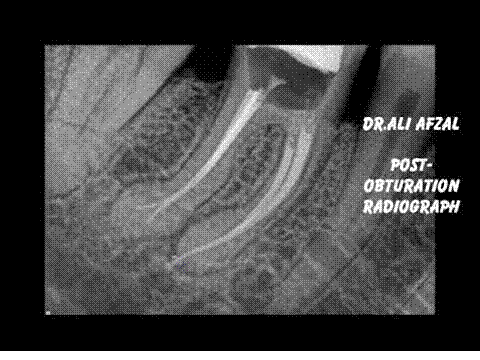
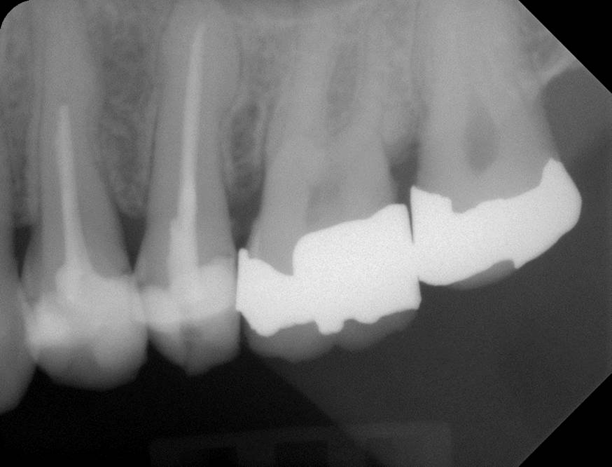
No treatment is necessary.
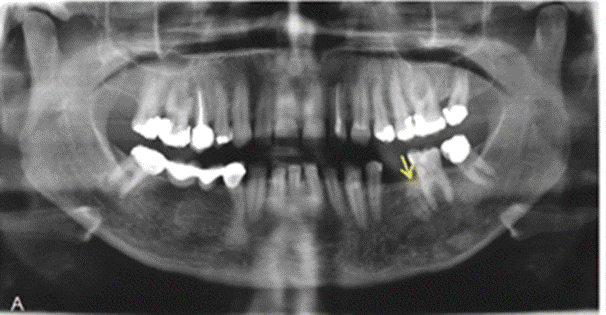
A: Routine orthopantomographic radiography depicting irregular osseous sclerotic lesion (arrow) in the vicinity of the mesial root surface of the 36 mandibular molar.
An unusual hypercementosis within the empty distal root tooth space of the second mandibular premolar, as well as the proliferation of odontogenic epithelium associated with a fragmented retained apical root remnant years after extraction of the tooth, mimicking a neoplasm.