Amelogenesis imperfecta
It is a group of clinically and genetically heterogeneous disorders that affect the development of enamel and result in abnormalities of the amount, composition, and/or structure of enamel. AI is classified into three main types that are related to the stages of the tissue formation process.

A and B, Amelogenesis imperfecta, hypoplastic type.
Amelogenesis imperfecta Types |
Stages |
Clinical & radiographic |
Hypoplastic AI |
A fault in the secretory stage of amelogenesis |
Enamel that is thinner than normal and that contrasts normally from dentine in the radiographic analysis |
Hypocalcified AI |
An alteration in the initial mineralization of the secretory stage |
The enamel initially develops normal thickness, is orange-yellow at eruption and consists of a poorly calcified matrix that is rapidly lost during normal function. The enamel has a lower radiopacity than the dentin |
Hypomature AI |
The defect occurs in the maturation stage of the enamel |
Enamel of normal thickness but has a mottled appearance; is slightly softer than normal enamel; and chips from the crown. Radiographically,it presents with approximately the same radiodensity as that of dentin. |

Amelogenesis imperfecta, hypoplastic, hypomaturation, and hypocalcification type in a Thai patient who had a mutation in the TP63 gene and was affected with the split hand–split foot-ectodermal dysplasia-amelogenesis imperfecta syndrome

Hypocalcified amelogenesis imperfecta. The enamel is soft and easily chipped away, leaving exposed dentin that is easily stained, worn, and caries prone.

Hypomaturation amelogenesis imperfecta. A, Severe form with enamel of normal thickness but that exhibits loss of translucency and hardness, resulting in some chipping of incisal edges. B, In the mild form the teeth may be relatively normal but contain white flecks in the incisal third of the teeth (snow-capped teeth)

Clinical subtypes of Amelogenesis Imperfecta found in this study; A, B, C: Clinical subtype of Hypoplastic Amelogenesis Imperfecta; D, E, F: Subtype of Hypomature AI; G, H, I: Subtype of Hypocalcified AI; J, K, L: Subtype of Hypomature-hypoplastic AI; M, N, O: Subtype of Hypocalcified-hypoplastic AI

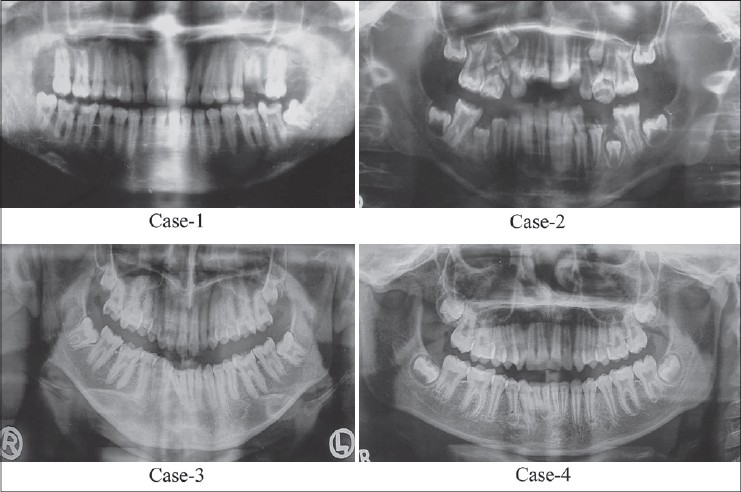
Case 1: OPG showed presence of a thin layer of enamel with radiodensity of enamel more than dentin. On the basis of clinical and radiographic features, final diagnosis of hypoplastic AI
Case 2: OPG showed presence of a thin layer of enamel with radiodensity of enamel more than dentin and taurodontism of 16, 26. Final diagnosis of hypoplastic-hypomaturation-AI with taurodontism of 16, 26 was made.
Case 3: Diagnosis of hypoplastic AI
Case 4: OPG showed presence of a thin layer of enamel with radiodensity of enamel more than dentin On the basis of clinical and radiographic features, final diagnosis of AI of hypomaturation type.